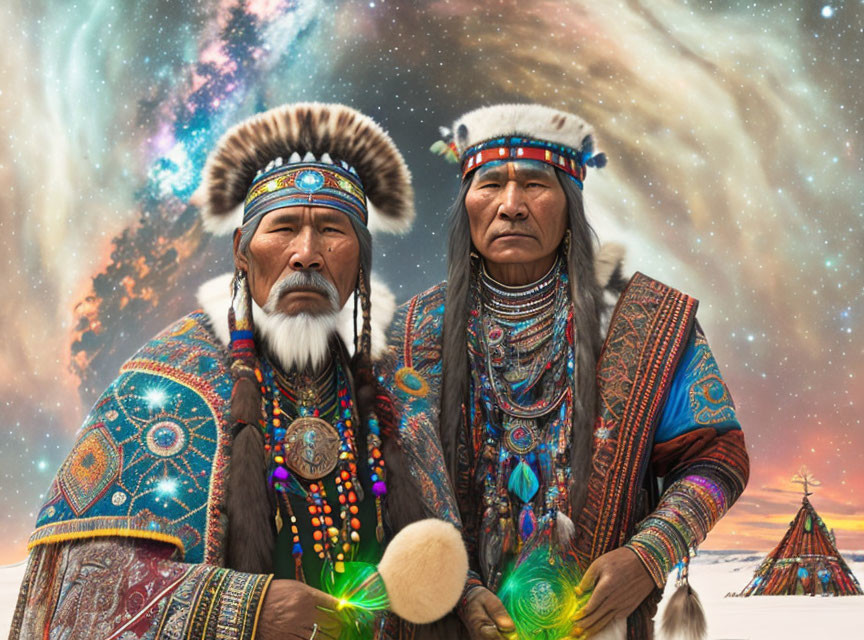
Shamans and medicine men are both spiritual and cultural leaders who act as healers and counselors in their communities. While the two terms are often used interchangeably, they have distinct differences in their practices and origins.
Shamanism is a spiritual practice that is believed to have originated in Siberia over 10,000 years ago. The term “shaman” comes from the Tungus language of the indigenous people of Siberia, and refers to a person who has the ability to communicate with the spirit world. Shamans use a variety of techniques to enter altered states of consciousness, such as drumming, dancing, and fasting, in order to access the spiritual realm and connect with spirits. They may also use herbs, crystals, and other natural substances to aid in their healing work.
In contrast, medicine men are spiritual leaders who are found in many different cultures around the world. They are typically recognized for their ability to heal physical ailments, and may use a combination of traditional healing practices and modern medicine to treat their patients. Medicine men can be found in both indigenous and non-indigenous cultures, and their practices are often influenced by the cultural traditions of their communities.
While there are many similarities between shamans and medicine men, there are also some key differences. Shamans are typically recognized for their ability to communicate with the spirit world, while medicine men are known for their physical healing abilities. Additionally, shamanism has a more specific cultural and historical origin in Siberia, while the concept of the medicine man is more widespread and varied across different cultures.
Overall, both shamans and medicine men play important roles in their communities as spiritual leaders and healers. While their practices and origins may differ, they share a common goal of promoting health and well-being for their communities.